Hackware.ru
Содержание:
- Nmap features
- Как пользоваться Nmap для сканирования портов в Linux
- Nmap Network Scanning
- Скриптовый движок Nmap(NSE — Nmap Scripting Engine)
- Nmap Network Scanning
- Chapter 12. Zenmap GUI Users’ Guide
- Introduction
- Linux RPM Source and Binaries
- Запускать Nmap с правами root или от обычного пользователя?
- Acknowledgments
- Завершён перевод документации по опциям Nmap
- The Girl with the Dragon Tattoo
- Example run and screen shots
- Reviews
- Top 5 Improvements in Nmap 5
Nmap features
This powerful tool carries many features that can be used by a hacker to get a lot of information about their targeted machine.
- Identify open ports.
- Network Inventory.
- Map a network.
- Exploiting and finding a vulnerability.
- Host uptime monitoring.
- Network security audit.
- Detecting OS.
- Detect service and version.
Network Mapping – It can be beneficial for you to check the devices present on a network including all the routers, servers, and switches and to verify how they are connected physically. Nmap on windows has the capability to show a whole map of the network.
Detecting OS – Nmap can also be used for OS footprinting. You can check the operating system running on your targeted device, including the vendor name and the version of the system. It can also give you an estimate for the ‘devices’ up-time.
Security Auditing – After footprinting the OS and knowing the applications running on the system, network managers now discover the vulnerability that can lead to specific flaws.
Discovering services – By using Nmap you can do more than just finding hosts on the network, you can also check their behavior that whether they are acting as web servers or mail servers and information regarding the version of the software they are using.
Как пользоваться Nmap для сканирования портов в Linux
Дальше рассмотрим примеры nmap. Сначала давайте рассмотрим как найти все подключенные к сети устройства, для этого достаточно использовать опцию -sL и указать маску нашей сети. в моем случае это 192.168.1.1/24. Маску вашей локальной сети вы можете найти, выполнив команду:
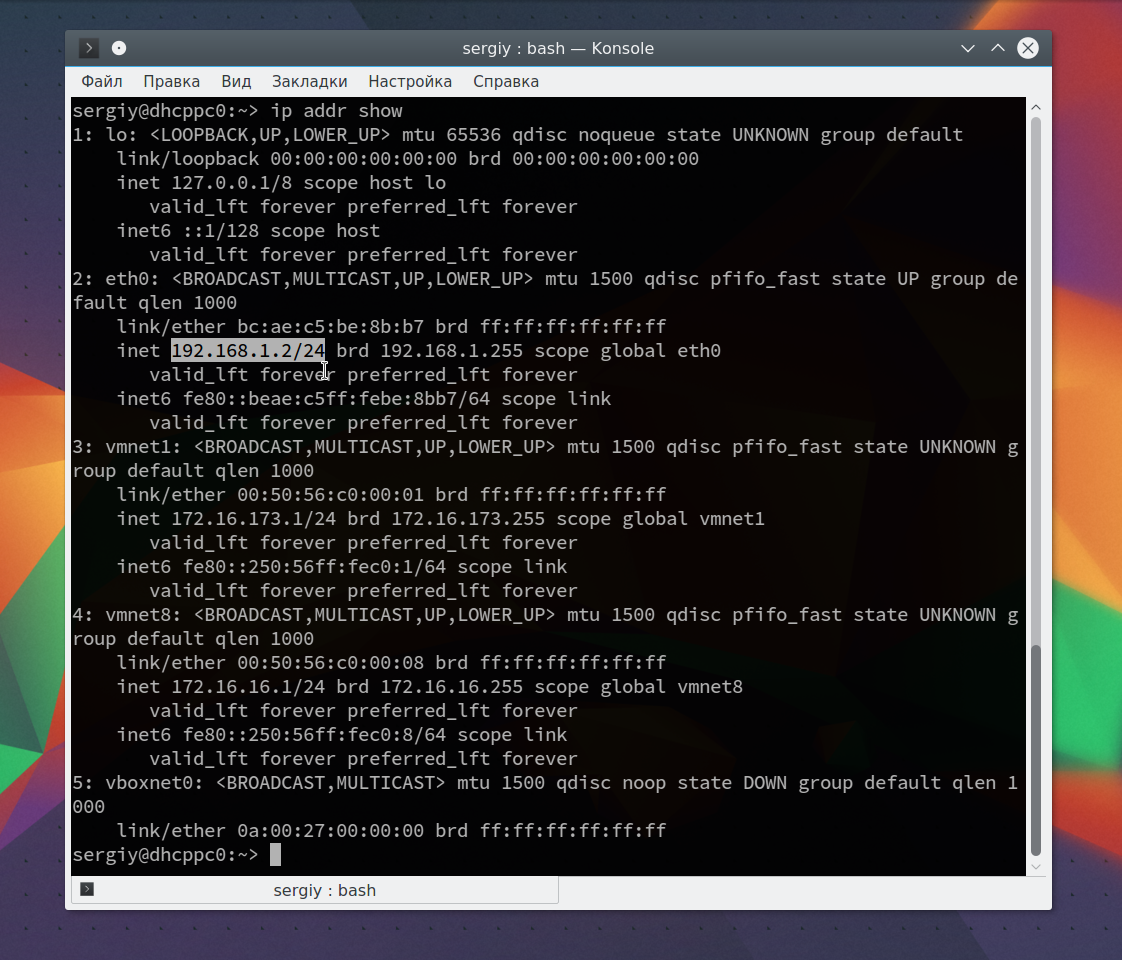
Из вывода для используемого интерфейса возьмите число после слеша, а до слэша укажите ip вашего роутера. Команда на сканирование сети nmap будет выглядеть вот так:
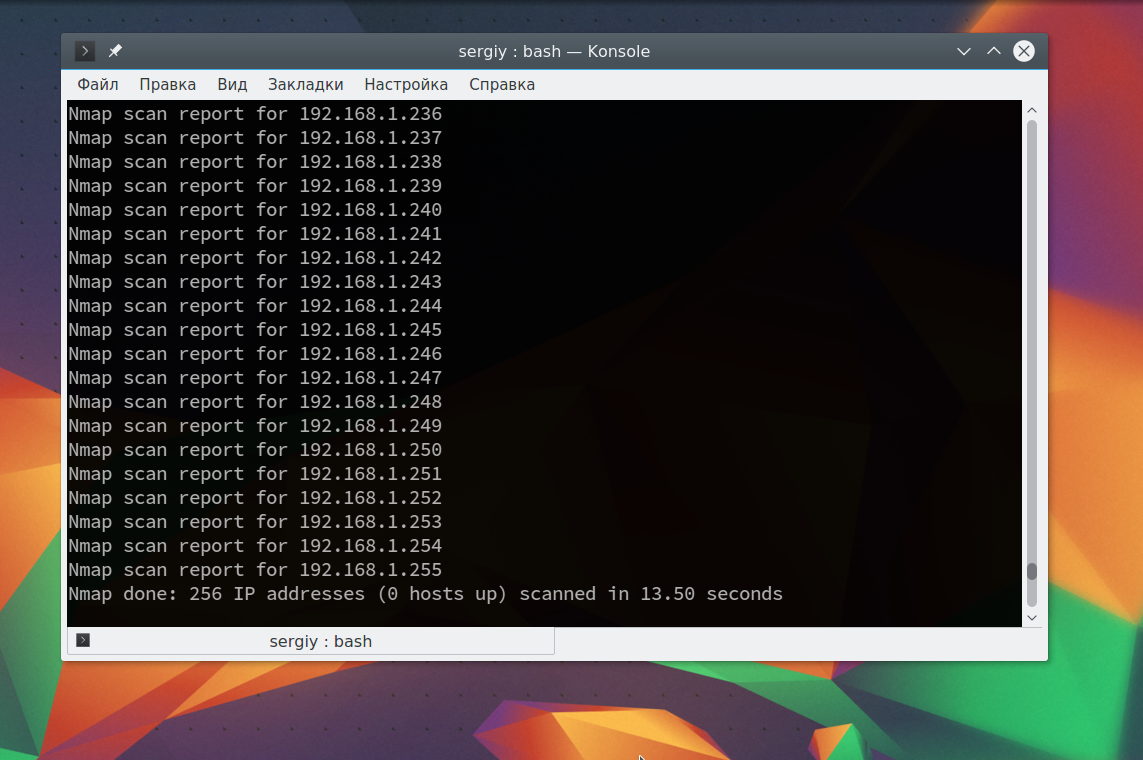
Иногда это сканирование может не дать никаких результатов, потому что некоторые операционные системы имеют защиту от сканирования портов. Но это можно обойти, просто использовав для сканирования ping всех ip адресов сети, для этого есть опция -sn:
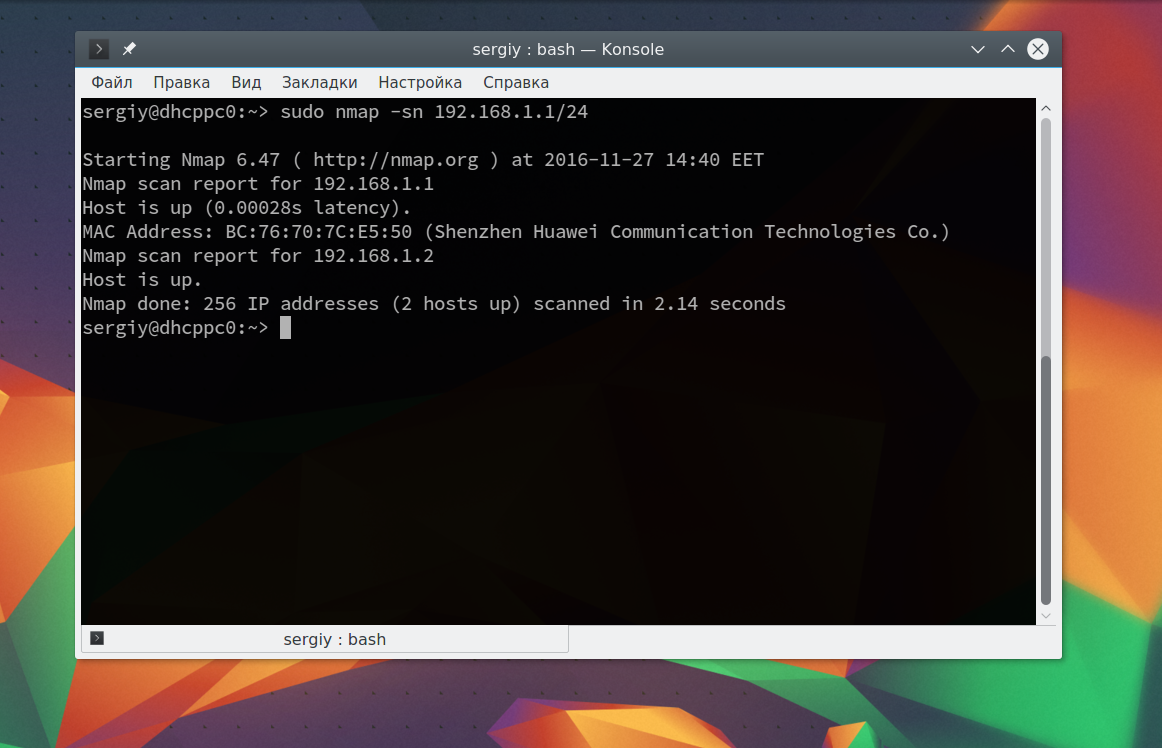
Как видите, теперь программа обнаружила активные устройства в сети. Дальше мы можем сканировать порты nmap для нужного узла запустив утилиту без опций:
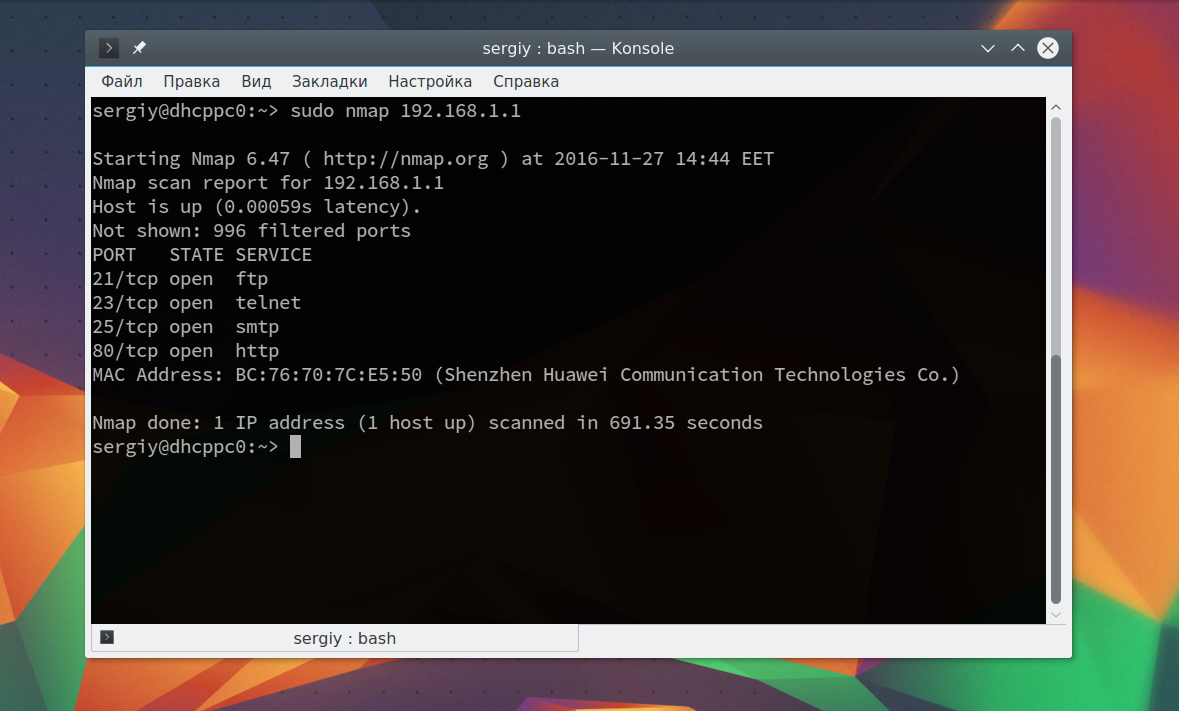
Теперь мы можем видеть, что у нас открыто несколько портов, все они используются каким-либо сервисом на целевой машине. Каждый из них может быть потенциально уязвимым, поэтому иметь много открытых портов на машине небезопасно. Но это еще далеко не все, что вы можете сделать, дальше вы узнаете как пользоваться nmap.
Чтобы узнать более подробную информацию о машине и запущенных на ней сервисах вы можете использовать опцию -sV. Утилита подключится к каждому порту и определит всю доступную информацию:
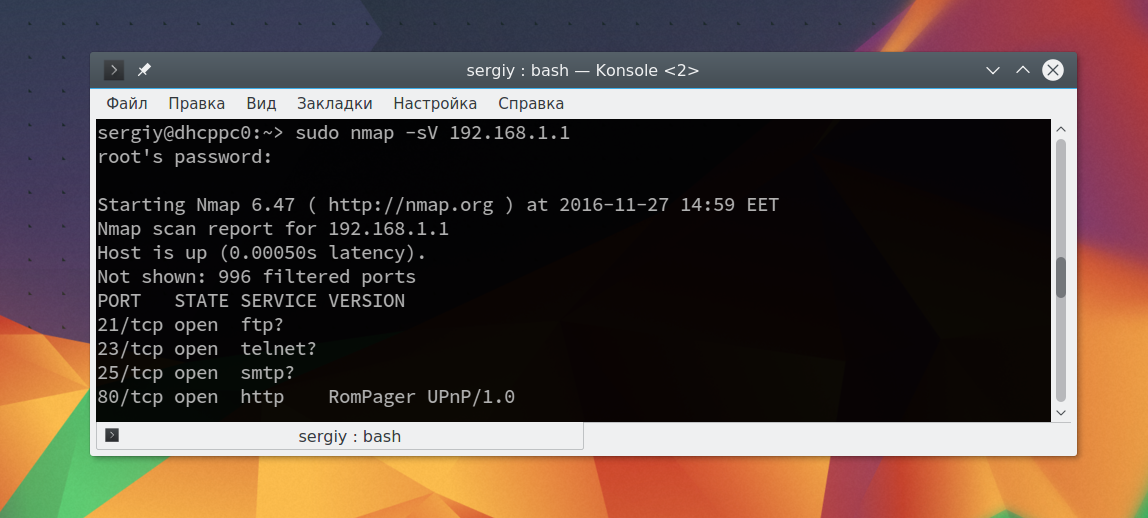
На нашей машине запущен ftp, а поэтому мы можем попытаться рассмотреть эту службу подробнее с помощью стандартных скриптов nmap. Скрипты позволяют проверить порт более детально, найти возможные уязвимости. Для этого используйте опцию -sC и -p чтобы задать порт:
Мы выполняли скрипт по умолчанию, но есть еще и другие скрипты, например, найти все скрипты для ftp вы можете командой:
Затем попытаемся использовать один из них, для этого достаточно указать его с помощью опции —script. Но сначала вы можете посмотреть информацию о скрипте:
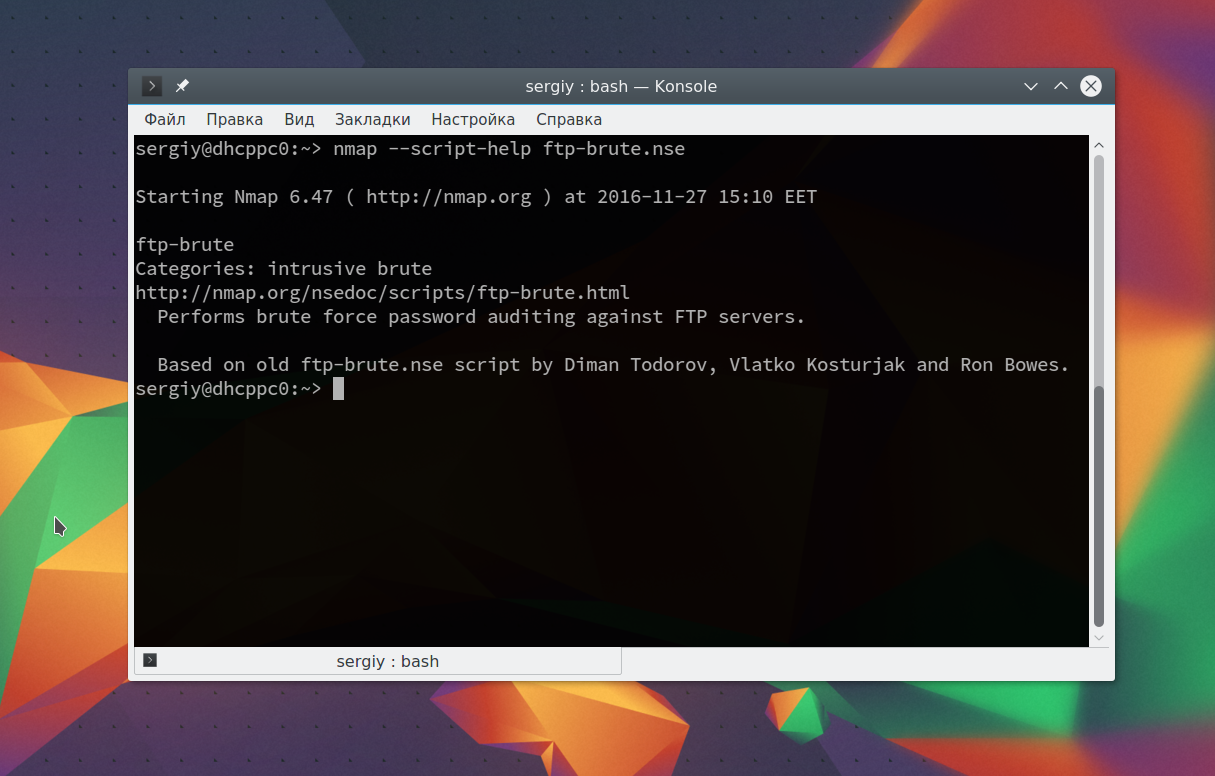
Этот скрипт будет пытаться определить логин и пароль от FTP на удаленном узле. Затем выполните скрипт:
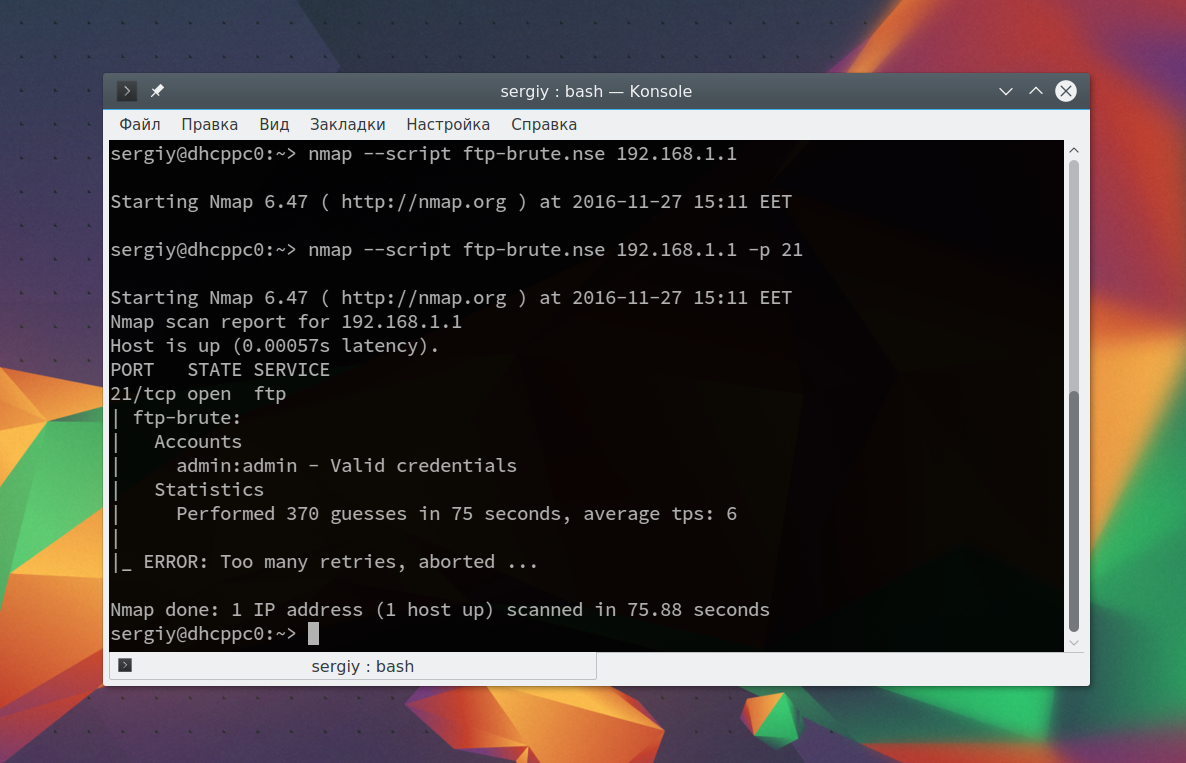
В результате скрипт подобрал логин и пароль, admin/admin. Вот поэтому не нужно использовать параметры входа по умолчанию.
Также можно запустить утилиту с опцией -A, она активирует более агрессивный режим работы утилиты, с помощью которого вы получите большую часть информации одной командой:
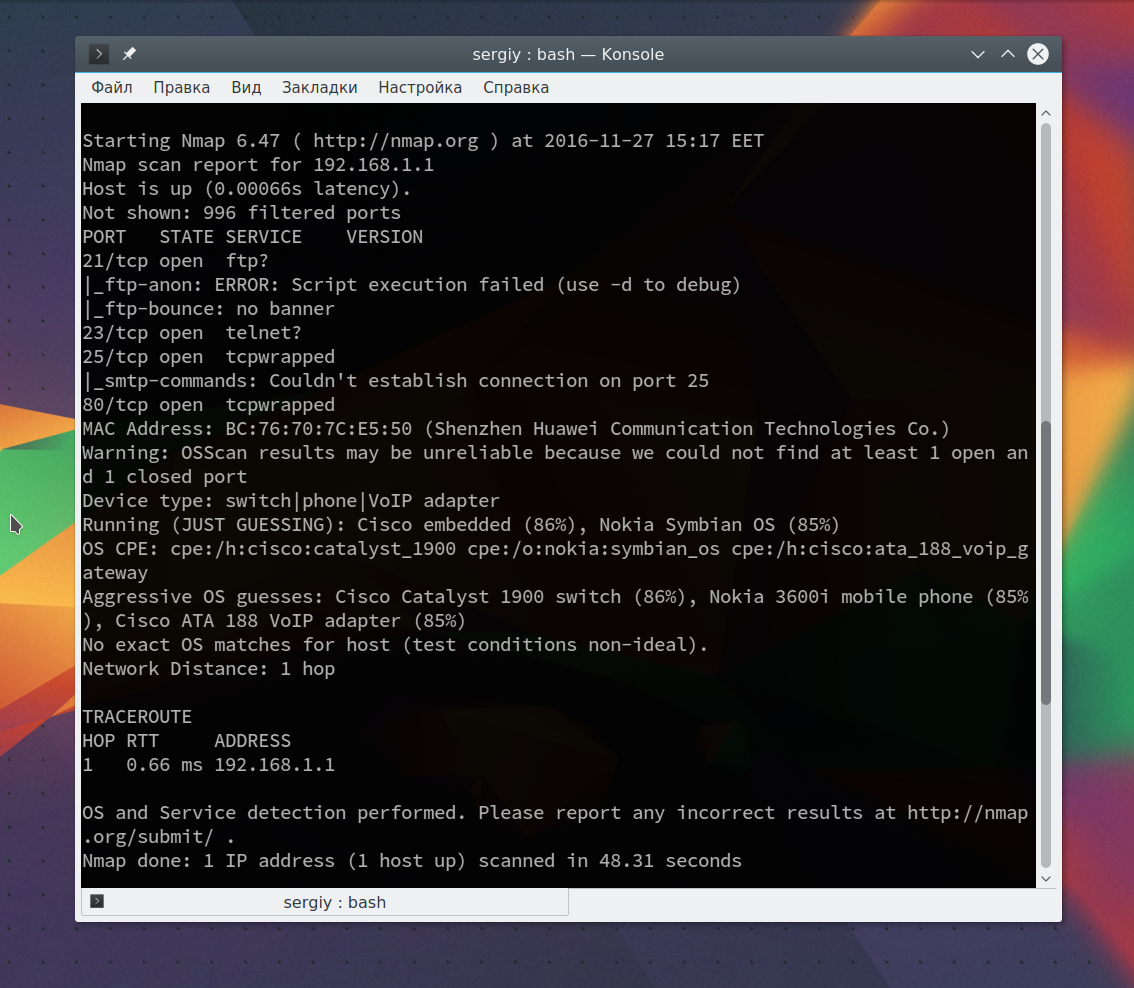
Обратите внимание, что здесь есть почти вся информация, которую мы уже видели раньше. Ее можно использовать чтобы увеличить защиту этой машины
Nmap Network Scanning
| Скриптовый движок Nmap(NSE — Nmap Scripting Engine) | ||
|---|---|---|
Скриптовый движок Nmap(NSE — Nmap Scripting Engine)
Скриптовый движок Nmap (NSE) это одна из наиболее мощных и гибких возможностей Nmap. Он позволяет
пользователям писать (и делиться ими) простые скрипты (используя
язык программирования Lua,
) для автоматизации
широкого круга сетевых задач. Эти скрипты выполняются со скоростью и эффективность ожидаемой вами от Nmap.
Пользователи могут использовать разнообразный и постоянно расщиряющийся набор скриптов, которые поставляются
вместе с Nmap, или написать свои скрипты под свои собственные нужды.
Когда мы создавали эту систему, считалось, что она будет использоваться для задач исследования сети, более
изощренного варианта определения версии, исследования уязвимостей. NSE может быть исполльзован даже для
обнаружения уязвимостей.
Чтобы отразить все многообразие возможностей использования скриптов и при этом упростить выбор необходимого
скрипта, каждый из них содержит поле, где указано к какой категории он принадлежит. Сейчас определены следующие
категории: ,
, ,
, ,
, и
. Все они описаны
в .
Скриптовый движок Nmap детально описан
на https://nmap.org/book/nse.html
и настраивается с помощью следующих опций:
-
Осуществляет сканирование на основе скриптов. Эквивалентно опции .
Некоторые их применяемых здесь скриптов относятся к категории intrusive (навязчивые) и не должны быть
использованы для сканирования целевой сети без разрешения. -
Осуществляет сканирование на основе скриптов (как ) используя разделенный запятыми список
категорий скриптов, отдельных файлов скриптов или директорий содержащих скрипты вместо стандартного набора скриптов.
Сначала Nmap пытается интерпретирует все аргументы как категории, затем (в случае неудачи) как файлы или директории.
Файл скрипта или директория скриптов могут быть определны с использованием абсолютного или относительного пути.
Абсолютные пути используются так, как вы их зададите. Относительные пути будут определяться относительно:;
;
(не используется в Windows);
NMAPDATADIR/ или
. Также все эти папки будут проверяться на наличие поддиректорииЕсли вы определили директорию со скриптами, и она была найдена, то Nmap загружает все NSE
скрипты (все файлы с расширением ) из этой директории. Файлы без расширения
игнорируются. Nmap не производит рекурсивный поиск скриптов во всех
поддиректориях. Если вы указываете конкретный файл, то его расширение не обязательно должно быть
.По умолчанию скрипты Nmap хранятся в папке —
поддиректории основного каталого Nmap. Для большей производительности,
все скрипты проиндексированы в базе даннных ,где указано к какой категории или категориям принадлежит каждый скрипт. Для исполнения всех скриптов из базы данных
Nmap задайте атрибут .Злонамеренные скрипты запускатся не в «песочнице» (sandbox) и поэтому могут повредить вашу систему или нарушить
вашу анонимность. Никогда не используйте скрипты от третьих лиц до тех пор, пока не будете доверять автору или
сами тщательно просмотрите скрипт. -
Позволяет вам передавать аргументы NSE скриптам. Аргументы передаются как пары
. Передаваемый аргумент обрабатывается и хранится в Lua таблице,
к которой имеют доступ все скрипты. Имена передаются как строки (должны быть буквенно-цифровыми значениями) и
используются в качестве ключей в . Значения могут быть также строками
или в свою очередь таблицами (заключенными в ‘’ и
‘’). Такие подтаблицы позволяют переопределить аргументы для конкретных скриптов
(например, если вы хотите предоставить различным скриптам различные пары login/password). Например, вы можете
определить аргументы через запятые: ,
и
. Если вы хотите переопределить опцию для
скрипта, вы должны проиндексировать подтаблицу с помощью скрипта, т.к. это
единственный способ указать скрипту на наличие специального аргумента. -
Эта опция делает то же самое, что и , но на один ISO уровень выше.
Если задана эта опция, то все входящие и исходящие соединения, осуществляемые скриптом, выводятся на экран.
Выводимая информация включает в себя используемый коммуникационный протокол, источник, цель и переданные
данные. Если более 5% переданных данных невозможно вывести на экран, то вывод будет представлять собой
шестнадцатеричный (hex) дамп. -
Этой опцией обновляется база скриптов ,
которая используется Nmap для определения доступных скриптов по умолчанию и их категорий. Обновлять
базу необходимо, только если вы добавили или удалили NSE скрипты из директории
, или поменяли категорию какого-нибудь скрипта. Эта опция
обычно используется без аргументов: nmap —script-updatedb.
Nmap Network Scanning
| Chapter 12. Zenmap GUI Users’ Guide | ||
|---|---|---|
Chapter 12. Zenmap GUI Users’ Guide
Table of Contents
- Scanning
- Interpreting Scan Results
- Saving and Loading Scan Results
- Surfing the Network Topology
- The Profile Editor
- Host Filtering
- Searching Saved Results
- Comparing Results
- Zenmap in Your Language
- Files Used by Zenmap
- Description of
- Command-line Options
- History
Introduction
Zenmap is the official graphical user interface (GUI) for the Nmap Security
Scanner. It is a multi-platform, free and open-source application
designed to make Nmap easy for beginners to use while providing
advanced features for experienced Nmap users. Frequently used scans
can be saved as profiles to make them easy to run repeatedly. A
command creator allows interactive creation of Nmap command lines.
Scan results can be saved and viewed later. Saved scans can be
compared with one another to see how they differ. The results of
recent scans are stored in a searchable database. A typical Zenmap screen shot is shown in . See the official Zenmap web page for more screen shots.
Figure 12.1. Typical Zenmap screen shot
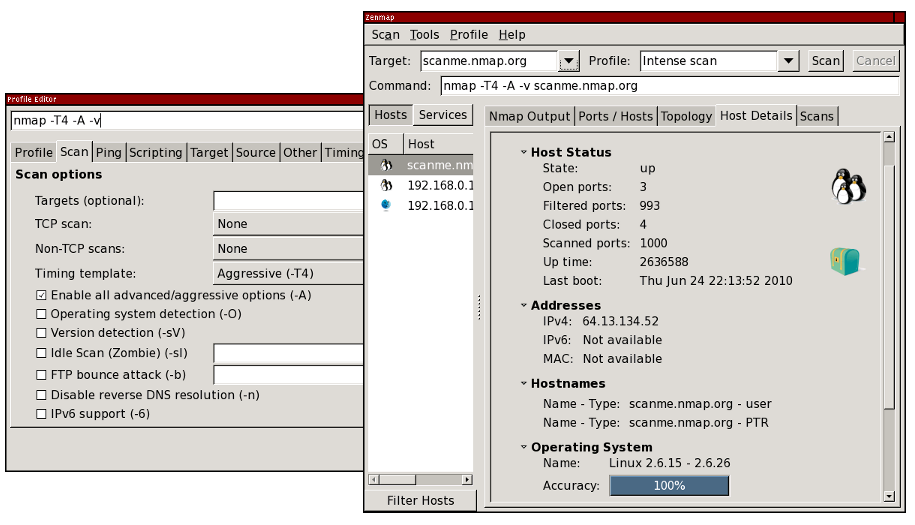
This guide is meant to make Nmap and Zenmap easy to use together,
even if you haven’t used either before. For the parts of this guide that
deal specifically with Nmap (command-line options and such), refer
to Chapter 15, Nmap Reference Guide.
The Purpose of a Graphical Frontend for Nmap
No frontend can replace good old command-line Nmap. The nature of a
frontend is that it depends on another tool to do its job. Therefore
the purpose of Zenmap is not to replace Nmap, but to make Nmap
more useful. Here are some of the advantages
Zenmap offers over plain Nmap.
- Interactive and graphical results viewing
-
In addition to showing Nmap’s normal output, Zenmap can
arrange its display to show all ports on a host or all hosts
running a particular service. It summarizes details about a
single host or a complete scan in a convenient
display. Zenmap can even draw a topology map of discovered
networks. The results of several scans may be combined
together and viewed at once. - Comparison
-
Zenmap has the ability to show the differences
between two scans. You can see what changed between the same
scan run on different days, between scans of two different
hosts, between scans of the same hosts with different
options, or any other combination. This allows
administrators to easily track new hosts or services
appearing on their networks, or existing ones going down. - Convenience
-
Zenmap keeps track of your scan results until you choose to
throw them away. That means you can run a scan, see the
results, and then decide whether to save them to a file. There
is no need to think of a file name in advance. - Repeatability
-
Zenmap’s command profiles make it easy to run the exact same
scan more than once. There’s no need to set up a shell script
to do a common scan. - Discoverability
-
Nmap has literally hundreds of options, which can be
daunting for beginners. Zenmap’s interface is designed to
always show the command that will be run, whether it comes
from a profile or was built up by choosing options from a
menu. This helps beginners learn and understand what they are
doing. It also helps experts double-check exactly what will be run before they press “Scan”.
Linux RPM Source and Binaries
Many popular Linux distributions (Redhat, Mandrake, Suse, etc) use
the RPM package management system for
quick and easy binary package installation. We have
written a detailed , though these simple commands usually do
the trick:
rpm -vhU https://nmap.org/dist/nmap-7.92-1.x86_64.rpm rpm -vhU https://nmap.org/dist/zenmap-7.92-1.noarch.rpm rpm -vhU https://nmap.org/dist/ncat-7.92-1.x86_64.rpm rpm -vhU https://nmap.org/dist/nping-0.7.92-1.x86_64.rpm
Latest stable release:x86-64 (64-bit Linux) Nmap RPM: nmap-7.92-1.x86_64.rpmx86-64 (64-bit Linux) Ncat RPM: ncat-7.92-1.x86_64.rpmx86-64 (64-bit Linux) Nping RPM: nping-0.7.92-1.x86_64.rpm
Optional Zenmap GUI (all platforms): zenmap-7.92-1.noarch.rpm
Source RPM (includes Nmap, Zenmap, Ncat, and Nping): nmap-7.92-1.src.rpm
Запускать Nmap с правами root или от обычного пользователя?
Программу Nmap можно запускать с привилегиями суперпользователя:
sudo nmap 91.235.129.250
Или с привилегиями обычного пользователя:
nmap 91.235.129.250
На первый взгляд может показаться, что разницы нет, поскольку программа в любом случае возвращает результат. Но на самом деле при запуске от root программа Nmap может отправлять сырые пакеты с помощью которых сканирование является менее заметным: используются полуоткрытые соединения, которые приложения, прослушивающие порт, обычно вообще не замечают (но могут заметить файерволы и другое специальное сетевое оборудование).
При запуске от обычного пользователя, Nmap использует системный вызов и открывает полноценное соединение, что является более заметным и более медленным.
Некоторые виды сканирования невозможно запустить от пользователя с обычными правами! В этом случае программа выведет:
Acknowledgments
A free open source scanner as powerful as Nmap is only possible
thanks to the help of hundreds of developers and other contributors.
We would like to acknowledge and thank the many people who contributed
ideas and/or code since Nmap 4.50. Special thanks go out to:
4N9e Gutek, Aaron Leininger, Adriano Monteiro Marques, Allison Randal, Andrew J. Bennieston, Andy Lutomirski, Angico, Arturo Buanzo, Arturo Buanzo Busleiman, Benson Kalahar, Bill Pollock, Brandon Enright, Brian Hatch, Busleiman, Chad Loder, Chris Clements, Chris Gibson, Chris Leick,, Daniel Roethlisberger, David Fifield, David Moore, Diman Todorov, Diman Todorov,, Dinu Gherman, Doug Hoyte, Dragos Ruiu, Dudi Itzhakov, Eddie Bell, Emma Jane Hogbin, Fabio Pedretti, Felix Leder, Gisle Vanem, Gisle Vanem,, Guilherme Polo, Guz Alexander, HD Moore, Henri Doreau, Henri Doreau,, Henry Gebhardt, Ithilgore, Jabra, Jah, James Messer, Jason DePriest, Jeff Nathan, Jesse Burns, Joao Correa, Joao Medeiros, Josh Marlow, Jurand Nogiec, Kris Katterjohn, Lamont Jones, Lance Spitzner, Leslie Hawthorn, Lionel Cons, Marius Sturm, Martin Macok, Matt Selsky, Max Schubert, Michael Pattrick, Michal Januszewski, Mike Frysinger, Mixter, Nathan Bills, Patrick Donnelly, Philip Pickering, Pieter Bowman, Rainer Müller, Raven Alder, Robert Mead, Rob Nicholls, Ron Bowes, Sebastián García, Simple Nomad, Solar Designer, Stephan Fijneman, Steve Christensen, Sven Klemm, Tedi Heriyanto, Thomas Buchanan, Thorsten Holz, Tillmann Werner, Tim Adam, Tom Duffy, Tom Sellers, Trevor Bain, Tyler Reguly, Valerie Aurora, van Hauser, Venkat Sanaka, Vlad Alexa, Vladimir Mitrovic, Vlatko Kosturjak, Will Cladek, William McVey, Zhao Lei
We would also like to thank the thousands of people who
have submitted OS and service/version fingerprints, as well as
everyone who has found and reported bugs or suggested features.
Завершён перевод документации по опциям Nmap
В системах Linux документацию по Nmap можно посмотреть командой:
man nmap
Там содержится полный перечень опций с их подробным описанием, причём на русском языке.
Но проблема в том, что русскоязычный вариант не обновлялся как минимум 10 лет!
В 2016 было решено актуализировать русскоязычную справку по опциям Nmap на странице . За основу была взята актуальная справка на английском. Была сделана сверка с русской версией и она использовалась для уже переведённых фрагментов.
Был начат перевод отсутствующих в русской версии фрагментов, одновременно отслеживался чейнджлог Nmap для добавления информации о новых опциях.
В результате:
— по сравнению с оригинальной русской версией дополнена информация по уже присутствующим опциям
— добавлены новые опции с описанием, которые полностью отсутствуют в русскоязычной справке, в частности:
- —discovery-ignore-rst
- —defeat-icmp-ratelimit
- —resolve-all
- —script-timeout
- —data
- —data-string
- —exclude-ports
- —disable-arp-ping
- —nsock-engine
- —script-args-file
Теперь полную, актуальную справку по опциям Nmap на русском языке вы можете прочитать на странице:
The Girl with the Dragon Tattoo
The Girl with the Dragon Tattoo (Swedish: Män som hatar kvinnor) is a 2009 Swedish thriller film (Wikipedia,
IMDB, Amazon) based on the Internationally bestselling novel by Stieg Larsson. It follows Lisbeth, a troubled young hacker suffering from Asperger syndrome and a history of abuse by authority figures, as she works with a journalist trying to solve a 40-year old murder mystery. It was the third-highest grossing non-English film of 2009.
The Nmap scene lasts only moments and occurs about 6 minutes in. Note that this is the original film (English subtitled version available on Amazon). A big-budget Hollywood remake was released in 2011 (IMDB, Wikipedia, Amazon), though they may have ruined it by cutting the Nmap scene!.
Trailer for the 2010 US/UK subtitled release:
Example run and screen shots
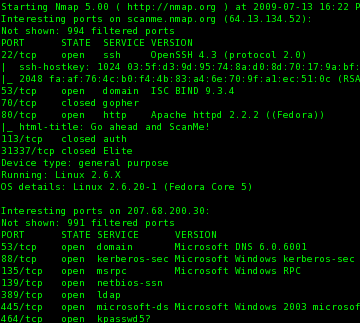
Nmap 5.00 provides a wealth of information about remote systems, as shown in this sample scan:
# nmap -A -T4 scanme.nmap.org 207.68.200.30 Starting Nmap 5.00 ( http://nmap.org ) at 2009-07-13 16:22 PDT Interesting ports on scanme.nmap.org (64.13.134.52): Not shown: 994 filtered ports PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION 22/tcp open ssh OpenSSH 4.3 (protocol 2.0) | ssh-hostkey: 1024 03:5f:d3:9d:95:74:8a:d0:8d:70:17:9a:bf:93:84:13 (DSA) |_ 2048 fa:af:76:4c:b0:f4:4b:83:a4:6e:70:9f:a1:ec:51:0c (RSA) 53/tcp open domain ISC BIND 9.3.4 70/tcp closed gopher 80/tcp open http Apache httpd 2.2.2 ((Fedora)) |_ html-title: Go ahead and ScanMe! 113/tcp closed auth 31337/tcp closed Elite Device type: general purpose Running: Linux 2.6.X OS details: Linux 2.6.20-1 (Fedora Core 5) Interesting ports on 207.68.200.30: Not shown: 991 filtered ports PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION 53/tcp open domain Microsoft DNS 6.0.6001 88/tcp open kerberos-sec Microsoft Windows kerberos-sec 135/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC 139/tcp open netbios-ssn 389/tcp open ldap 445/tcp open microsoft-ds Microsoft Windows 2003 microsoft-ds 464/tcp open kpasswd5? 49158/tcp open ncacn_http Microsoft Windows RPC over HTTP 1.0 49175/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC Running: Microsoft Windows 2008|Vista Host script results: | smb-os-discovery: Windows Server (R) 2008 Enterprise 6001 Service Pack 1 | LAN Manager: Windows Server (R) 2008 Enterprise 6.0 | Name: MSAPPLELAB\APPLELAB2K8 |_ System time: 2009-07-13 16:17:07 UTC-7 | nbstat: NetBIOS name: APPLELAB2K8, NetBIOS user: , NetBIOS MAC: 00:1a:a0:9a:a3:96 | Name: APPLELAB2K8 Flags: |_ Name: MSAPPLELAB Flags: TRACEROUTE (using port 135/tcp) HOP RTT ADDRESS 9 36.88 ge-10-0.hsa1.Seattle1.Level3.net (4.68.105.6) 10 36.61 unknown.Level3.net (209.245.176.2) 11 41.21 207.68.200.30 Nmap done: 2 IP addresses (2 hosts up) scanned in 120.26 seconds # (Note: some output was modified to fit results on screen)
Here are some Nmap and Zenmap 5.00 screen shots (click thumbnails for full resolution):
 Classic command-line Nmap |
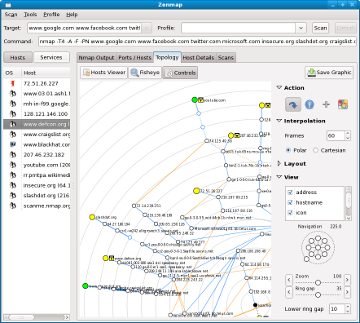 Zenmap’s new network topology graphing mode |
 Zenmap showing all discovered HTTP services |
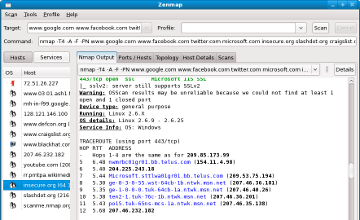 Zenmap displaying Nmap output |
Reviews
Reviews are posted here as they come in. Please let me know if you post a review to your blog or anywhere else.
-
“If you are looking for the book on Nmap, the search is over: NNS is a winner”—Richard Bejtlich’s detailed review. NNS also made Bejtlich’s Top Books of 2008 list.
-
“This is the ultimate Nmap reference guide” on “Nmap, the legendary network scanner”—Ben Rothke’s Slashdot review.
-
“Released for sale on Amazon on December 6th and already number 1 best seller in the Computer books category, this is the MUST-HAVE book on network scanning.”—David Heath’s review for ITWire.
-
“This is the most revealing technical book I’ve ever read about a security tool. Fyodor turns Nmap inside out to explain what it does, how it does it and why it was written that way. If you are looking for a definitive book on Nmap, this is it.”—Ethan Ten’s 5-star Amazon UK review.
-
“Some light reading”—Metasploit author HD Moore.
-
Nmap Network Scanning “is required reading for anyone securing a network” and “should be front and center on your desk for months and years to come”—Wireshark University founder Laura Chappell’s glowing review.
-
NNS is “a must-have book to get the most out of NMAP”, filled with examples and analysis that are “like looking over an expert’s shoulder”—Mike Fratto’s glowing and informative Information Week review.
-
“I am amazed that after all these years I still learn stuff about nmap. The book is good and you should buy it!”—David Maynor
-
NNS will “quickly become required reading for network engineers, system administrators, and anyone working in the computer security arena….I have been using nmap for nearly a decade and there were still some great tips and tricks that I found for the first time in these pages.”—Eddie Block’s 5-star Amazon review.
-
“Nmap is simply a required
tool in the IT toolbox. Similarly, this book is required reading for
anyone in IT to get the most out of that tool.”—About.com network security expert Tony Bradley’s detailed 5-star review. -
“The book goes into the detail you would expect with the sort of information that true afficianadoes lust after” while being “easy and fun to read with great examples along the way”—David Pybus’s 5-star Amazon UK review.
-
“I would recommend this as a must-have book for any network or security professional, as well as anyone wanting to learn more about TCP/IP”—JP Bourget’s very detailed Ethical Hacker Network review.
-
Fyodor does an outstanding job covering everything from the most basic use of nmap, through advanced topics, such as evading detection”—Jon R. Kibler’s enthusiastic review on the pen-test list.
-
“Fyodor’s absolute, incredibly definitive guide on
Nmap will imbue you with rock-solid scanning
stratagems”—Josef
Chamberlin’s 5-star
Amazon review. -
NNS is “The wealth of information contained in this book will have even hardcore nmap experts learning a thing or two about the preeminent network scanner.”—Brad Berkemier’s review, which also calls NNS “engaging and informative” and “the ultimate nmap guide”.
-
“Nmap Network Scanning is a masterpiece that teaches the reader the Art of Network Mapping and Scanning … one of the best books I’ve read in years.”—Raul Siles’ review.
- Foreign Coverage: Barrapunto (Spanish), Tecnozona (Spanish), Binary Zone (Arabic)
Top 5 Improvements in Nmap 5
Before we go into the , here
are the top 5 improvements in Nmap 5:
-
The new Ncat tool aims to be
your Swiss
Army Knife for data transfer, redirection, and debugging. We
released a
whole users’ guide
detailing security testing and network administration tasks made easy with Ncat. -
The addition of the Ndiff scan
comparison tool completes Nmap’s growth into a whole suite of
applications which work together to serve network administrators and
security practitioners. Ndiff makes it easy to automatically scan
your network daily and report on any changes (systems coming up or
going down or changes to the software services they are running). The
other two tools now packaged with Nmap itself are Ncat and
the Zenmap GUI and results
viewer. -
Nmap performance has . We spent last summer scanning much of the Internet
and merging that data with internal enterprise scan logs to determine
the most commonly open ports. This allows Nmap to scan fewer ports by
default while finding more open ports. We also added a fixed-rate
scan engine so you can bypass Nmap’s congestion control algorithms and
scan at exactly the rate (packets per second) you specify. -
We released Nmap Network
Scanning, the official Nmap guide to network discovery and security
scanning. From explaining port scanning basics for novices to
detailing low-level packet crafting methods used by advanced hackers,
this book suits all levels of security and networking professionals. A
42-page reference guide documents every Nmap feature and option, while
the rest of the book demonstrates how to apply those features to
quickly solve real-world tasks. More than half the book
is available in the free
online edition. -
The Nmap Scripting
Engine (NSE) is one of Nmap’s most powerful and flexible
features. It allows users to write (and share) simple scripts to
automate a wide variety of networking tasks. Those scripts are then
executed in parallel with the speed and efficiency you expect from
Nmap. All existing scripts have been improved, and 32 new ones added.
New scripts include a whole bunch of MSRPC/NetBIOS attacks, queries,
and vulnerability probes; open proxy detection; whois and AS number
lookup queries; brute force attack scripts against the SNMP and POP3
protocols; and . All NSE scripts
and modules are described in the
new NSE documentation portal.